What is OM5 fibre optic patch cable and what are the advantages and features in its application?
2021/1/26 14:00:55
Overview
OM5 fibre builds on OM3/OM4 fibre and extends its performance to support multiple wavelengths, OM5 fibre was originally designed to cope with the WDM requirements of multimode transmission systems. Therefore, its most valuable application is in the field of short wavelength division multiplexing. So let's talk about the advantages and applications of OM5.

1���、What is OM5 fiber optic patch cables
Fibre optic patch cords are used as patch cords from the equipment to the fibre optic cabling link with a thick protective layer. As data centre requirements for transmission rates continue to increase, OM5 fibre patch cords are beginning to be used more and more.
Originally known as Wideband Multimode Fibre Patchcord (WBMMF), OM5 is a new standard for fibre optic patchcords defined by TIA and IEC, with a fibre diameter of 50/125um, an operating wavelength of 850/1300nm and support for four wavelengths. In terms of construction, it is not significantly different from OM3 and OM4 fiber optic patch cords and is therefore fully backward compatible with traditional OM3 and OM4 multimode fiber optic patch cords.
2、Advantages of OM5 fibre optic patch cables
①High recognition: OM5 fiber optic patch cords were originally published by the Communications Industry Association as TIA-492AAAE and were unanimously accepted in the ANSI/TIA-568.3-D revision call for comments issued by the American National Standards Institute.
(ii) Scalability: OM5 fiber optic patch cords can combine shortwave wavelength division multiplexing (SWDM) and parallel transmission technologies in the future and can support 200/400G Ethernet applications with only 8 cores of wideband multimode fiber (WBMMF).
③Cost reduction: OM5 fiber optic patchcord draws on the WDM technology of single-mode fiber, extending the range of wavelengths available for network transmission, capable of supporting 4 wavelengths on 1 core of multimode fiber, reducing the number of fiber cores required to 1/4 of the previous one, which largely reduces the cabling cost of the network.
High compatibility and interoperability: OM5 fiber patch cable can support traditional applications as well as OM3 and OM4 fiber patch cables, and it is fully compatible and highly interoperable with OM3 and OM4 fiber patch cables. With its low link cost, low power consumption and higher availability, H&T's multimode fibre with VCSEL is the most cost effective data centre solution for most enterprise users.
3、OM5 fibre optic patch cord applications
①Generally used for the connection between the optical terminal and the terminal box, and used in a number of applications such as fibre optic communication systems, fibre optic access networks, fibre optic data transmission and local area networks.
②OM5 fiber optic patch cords can be used for higher bandwidth applications. OM5 fiber optic patch cords are able to support higher bandwidths due to the significantly optimized manufacturing process of fiber optic preforms.
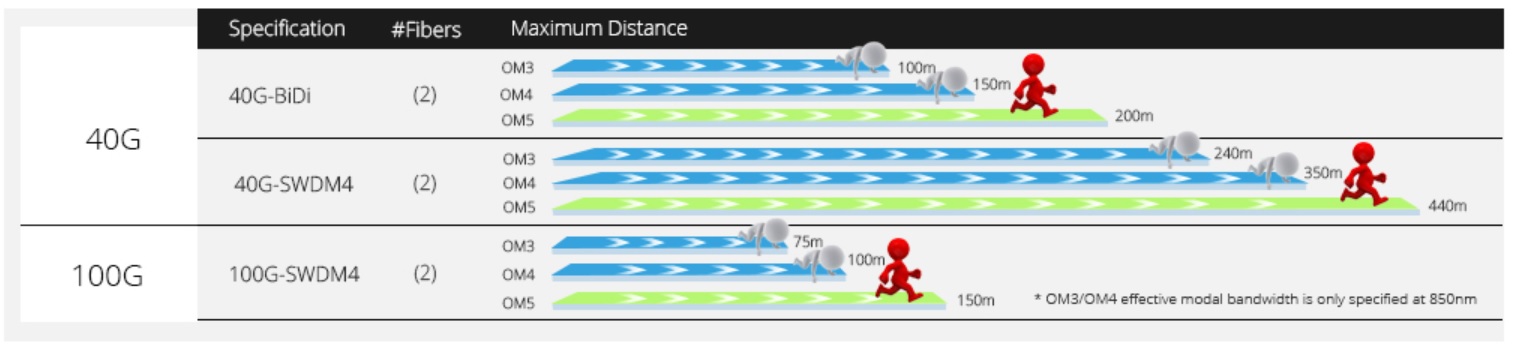
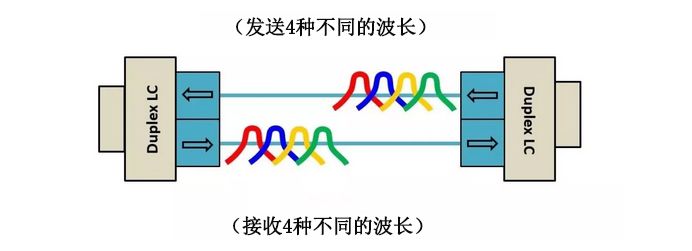
(iii) OM5 multimode fibres support more wavelength channels and are therefore in line with the development of SWDM4 with four wavelengths or BiDi technology with two wavelengths. Similar to BiDi for 40G links, SWDM transceivers require only a two-core LC duplex connection, with the difference that SWDM operates on four different wavelengths per fibre between 850nm and 940nm, with one fibre dedicated to transmitting signals and the other to receiving signals.
④For higher speed 400G Ethernet applications such as 400GBase-SR4.2 (4 pairs of fibers, 2 wavelengths, 50GPAM4 per channel) or 400GBase-SR4.4 (4 pairs of fibers, 4 wavelengths, 25GNRZ per channel), only 8 cores of OM5 fiber are required, compared to Compared to the first generation of 400G Ethernet 400GBase-SR16 (16 pairs of fibres, 25Gbps per channel), the number of fibres required is only a quarter of that of traditional Ethernet, and SR16 is a milestone in the development of multimode 400G technology, proving the possibility of multimode technology supporting 400G. The SR16 is a milestone in the development of multimode 400G technology, proving the possibility of multimode support for 400G.
4、To meet the needs of high-speed data centre transmission
OM5 fiber optic patch cable gives a strong life to mega data centre, it breaks through the traditional multimode fiber used in parallel transmission technology and low transmission rate bottleneck. Not only can it support higher speed network transmission with fewer multimode fibre cores, but, because it uses a lower cost shortwave wavelength, the cost and power consumption of the optical module is much lower than that of a single-mode fibre with a long-wave laser source. Therefore, as the transmission rate requirements continue to rise, by using short wavelength division multiplexing plus parallel transmission technology, data centre cabling costs will be greatly reduced, OM5 fibre patch cables will have a broad application prospect in the future 100G/400G/1T ultra-large data centres.
Multimode fibre has always been an efficient and flexible transmission medium, and the continuous development of new application potential for multimode fibre will enable it to adapt to higher speed transmission networks. The new industry standard defined OM5 fibre solution is optimised for multi-wavelength SWDM and BiDi transceivers, providing longer transmission links and network upgrade margins for high-speed transmission networks above 100Gb/s.
FAQ:
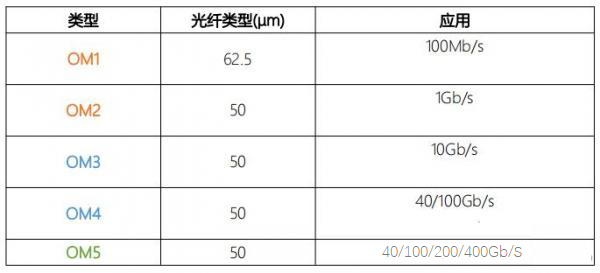
1. What is the difference between OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4 and OM5?
Generally speaking, OM1 is a conventional 62.5/125um; OM2 is a conventional 50/125um; OM3 is an 850nm laser-optimized 50um core diameter multimode fiber, which can reach 300m in 10Gb/s Ethernet using 850nm VCSEL; OM4 is an upgraded version of OM3, OM4 multimode fiber optimizes OM3 multimode The OM4 multimode fibre optimises the differential mode delay (DMD) generated by the OM3 multimode fibre at high transmission speeds, resulting in a significant increase in transmission distance, which can reach 550m; OM5 fibre patch cord is a new standard defined by TIA and IEC for fibre patch cords with a fibre diameter of 50/125μm, which can be used for higher bandwidth applications compared to OM3 and OM4 fibre patch cords. The bandwidth and maximum distance when transmitting differs between grades.
2. What is the difference between OM5 and OM3, OM4?
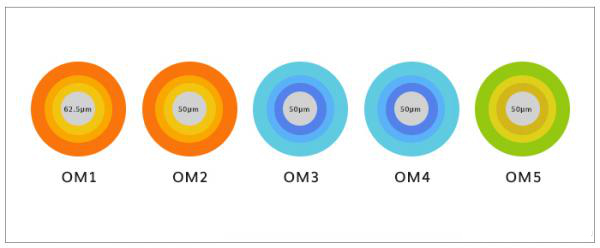
1. Different jacket colours
In order to differentiate between different fibre optic patch cords, different coloured outer jackets are used. For non-military use, single-mode fibres generally use a yellow outer jacket. In multimode fibres, OM1 and OM2 are orange, OM3 and OM4 are aqua blue and OM5 is aqua green.
2. Different application areas
OM1 and OM2 have been widely deployed for many years for in-building applications, supporting Ethernet paths up to 1GB; OM3 and OM4 cables are typically used in data centre cabling environments, supporting 10G and even 40/100G high-speed Ethernet paths. OM5 is designed for 40Gb/s and 100Gb/s transmission, reducing the number of fibres required for high-speed transmission.