Demystifying 25G SFP28 Transceiver Modules: A Comprehensive Guide
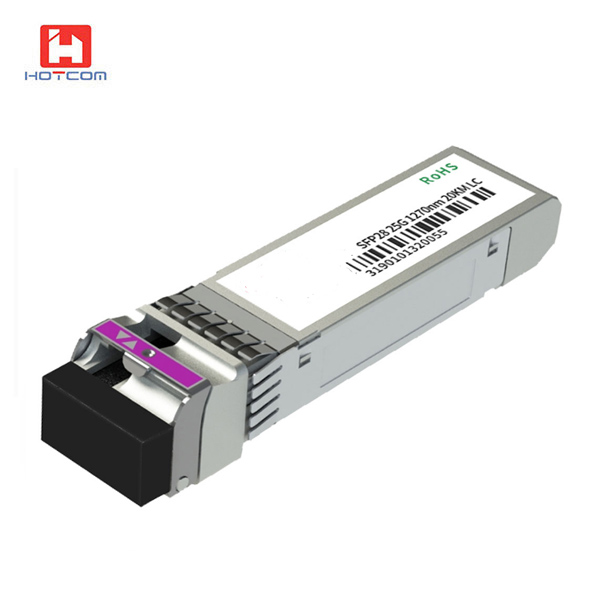
In the realm of high-speed data transmission, 25G SFP28 transceiver modules have emerged as a cornerstone of modern networking infrastructure. These compact, pluggable modules offer a cost-effective and versatile solution for connecting network devices at 25 gigabits per second (Gbps), making them a popular choice for data centers, enterprise networks, and service provider backbones.
Understanding the SFP28 Form Factor
Before delving into the intricacies of 25G SFP28 transceivers, it’s essential to grasp the SFP28 form factor, the physical housing that accommodates these modules. The Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) transceiver standard, introduced in 2001, has revolutionized the industry by providing a standardized and interoperable solution for connecting network devices. SFP28, the latest iteration of this standard, offers increased bandwidth and density compared to its predecessors, making it ideal for high-speed data applications.
Exploring 25G SFP28 Transceiver Types
The world of 25G SFP28 transceivers encompasses a diverse range of modules, each tailored to specific applications and distances. Here’s a breakdown of the primary types:
25G SFP28 SR (Short Reach): Designed for short-haul applications up to 100 meters, 25G SFP28 SR transceivers utilize multimode fiber (MMF) for data transmission. They are commonly used in data centers and enterprise networks for intra-rack and inter-rack connectivity.
25G SFP28 LR (Long Reach): Catering to longer distances up to 10 kilometers, 25G SFP28 LR transceivers employ single-mode fiber (SMF) for data transmission. They are well-suited for connecting data centers across campus environments or for enterprise network backhaul applications.
25G SFP28 ER (Extended Reach): Pushing the boundaries of reach, 25G SFP28 ER transceivers extend the transmission distance to an impressive 40 kilometers. They are ideal for connecting geographically dispersed network elements over long-haul links.
25G SFP28 CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing): Designed for cost-effective long-haul connectivity, 25G SFP28 CWDM transceivers utilize multiple wavelengths to multiplex data onto a single fiber, enabling up to 40 kilometers of transmission. They are particularly suitable for dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) systems.
25G SFP28 BiDi (Bidirectional): Employing a single fiber strand for both data transmission and reception, 25G SFP28 BiDi transceivers offer a cost-effective and space-saving solution for short-reach applications up to 10 kilometers. They are particularly useful in situations where fiber resources are limited.
Unveiling Key Specifications
25G SFP28 transceivers adhere to industry-standard specifications, ensuring interoperability and reliable performance across various network environments. Here are some of the critical specifications to consider:
Data Rate: The cornerstone of 25G SFP28 transceivers is their ability to transmit data at 25 gigabits per second (Gbps), enabling high-speed connectivity for demanding applications.
Transmission Distance: The maximum distance over which data can be reliably transmitted varies depending on the transceiver type. 25G SFP28 SR transceivers typically reach up to 100 meters, while 25G SFP28 ER transceivers can extend to 40 kilometers or more.
Connector Type: 25G SFP28 transceivers employ the LC connector type, ensuring compatibility with various fiber optic equipment.
Power Consumption: These transceivers typically consume low power, making them energy-efficient solutions.
Operating Temperature: 25G SFP28 transceivers operate within a wide temperature range, ensuring reliable performance in various environments.
Addressing Common Questions and Concerns
What are the advantages of 25G SFP28 transceivers over traditional 10G SFP+ transceivers?
25G SFP28 transceivers offer several compelling advantages over their 10G SFP+ predecessors:
a. Increased Bandwidth: 25G SFP28 transceivers provide double the bandwidth of 10G SFP+ transceivers, enabling faster data transfers and supporting emerging applications like 5G and cloud computing.
b. Future-Proofing: 25G SFP28 transceivers are well-positioned to meet the growing bandwidth demands of future technologies, making them a cost-effective and future-proof investment.
c. Reduced Cabling Requirements: 25G SFP28 transceivers can support twice the data traffic with the same number of cables compared to 10G SFP+ transceivers, simplifying cabling infrastructure and reducing costs.
d. Enhanced Power Efficiency: 25G SFP28 transceivers typically consume lower power per Gbps compared to 10G SFP+ transceivers, making them more energy-efficient and cost-effective in the long run.
What are the compatibility considerations when using 25G SFP28 transceivers?
When incorporating 25G SFP28 transceivers into your network infrastructure, it’s crucial to ensure compatibility across all network devices. Verify that both the transmitting and receiving devices support 25G SFP28 transceivers and that they are operating at the same wavelength combination. Consult the documentation of your network equipment for specific compatibility requirements.
How can I choose the right 25G SFP28 transceiver for my application?
Selecting the appropriate 25G SFP28 transceiver for your specific application depends on several factors:
a. Transmission Distance: Consider the distance between the connected devices. 25G SFP28 SR transceivers are suitable for short-reach applications, while 25G SFP28 LR and ER transceivers cater to longer distances.
b. Fiber Type: Determine the fiber type you are using. 25G SFP28 SR transceivers utilize multimode fiber (MMF), while 25G SFP28 LR, ER, and CWDM transceivers typically employ single-mode fiber (SMF).
c. Wavelength Combination: If using BiDi transceivers, ensure both devices support the same wavelength combination (e.g., 1270nm/1330nm or 1270nm/1310nm).
d. Network Requirements: Evaluate your network’s bandwidth demands and future growth projections to choose the appropriate data rate and transmission capabilities.
Conclusion
25G SFP28 transceiver modules have emerged as a transformative force in today’s high-speed networking landscape. Their ability to deliver 25 gigabits per second of data transmission, coupled with their versatility and compatibility across various network environments, makes them an indispensable component for data centers, enterprise networks, and service provider backbones. As the demand for bandwidth continues to surge, 25G SFP28 transceivers are poised to play an even more critical role in shaping the future of high-speed connectivity. By understanding the intricacies of these modules and their diverse applications, network administrators and IT professionals can make informed decisions to optimize their network infrastructure and support the ever-increasing demands of modern data-driven applications.a